A Deep Dive into Poverty, Life Expectancy and GDP (Gross Domestic Product) across African Countries
Introduction
Africa, a continent abundant in natural resources, continues to grapple with significant economic and social challenges, making it one of the most disadvantaged regions worldwide. The persistence of poverty, inadequate healthcare, and low life expectancy are among the critical issues confronting African nations. While progress has been made in recent years, urgent attention is required to address these persistent challenges.
Poverty, life expectancy, and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) are pivotal indicators that shed light on a country's economic and social conditions. In Africa, these indicators exhibit substantial variation among countries, making it complex to comprehend the intricate relationship between poverty, life expectancy, and GDP. This case study endeavors to delve deeply into the correlation among these indicators within African countries.
Questions answered in this analysis
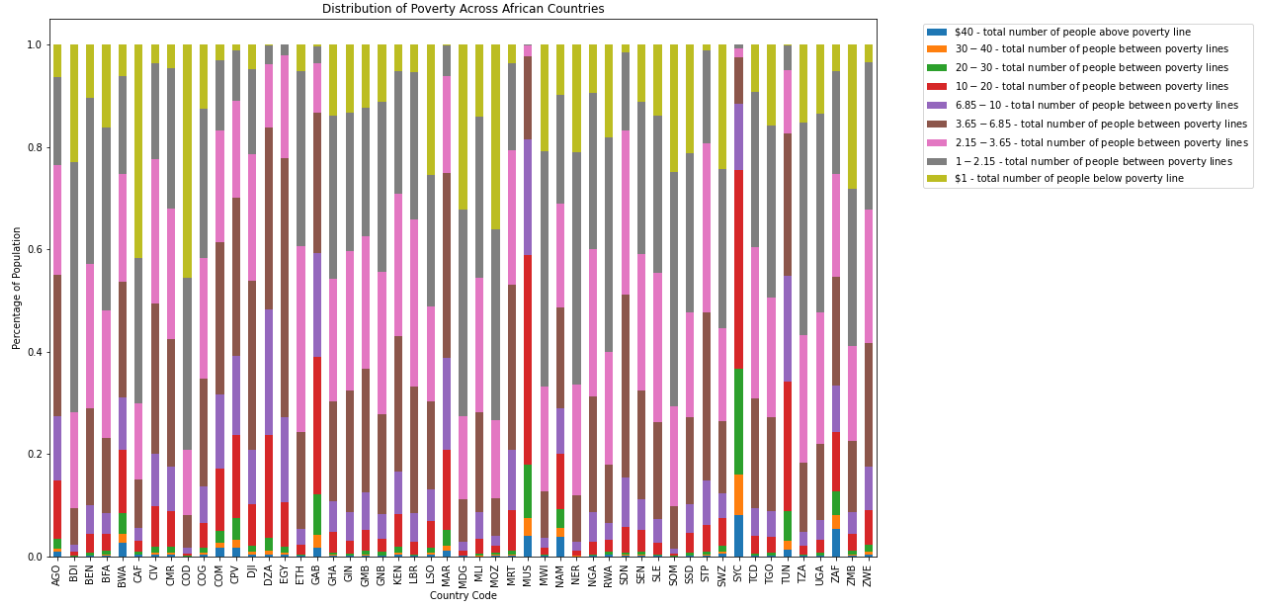
Question 1: What is the distribution of poverty across African countries?
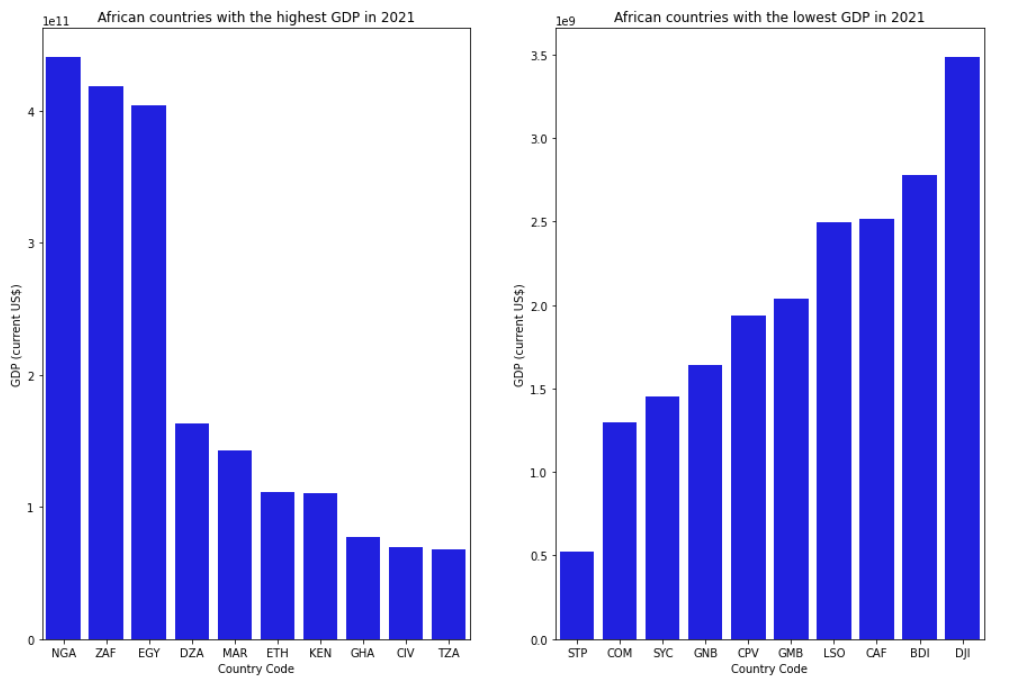
Question 2: Which African countries have the highest and lowest GDP?
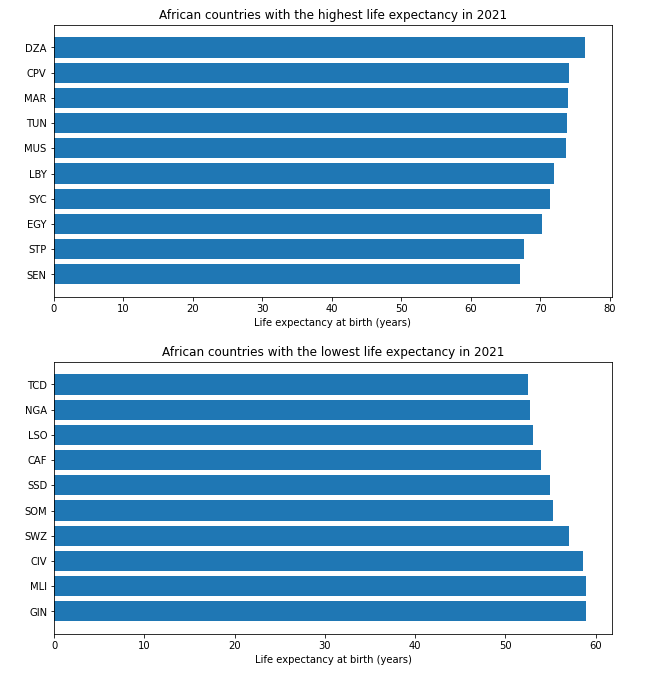
Question 3: Which African countries have the highest and lowest life expectancy?
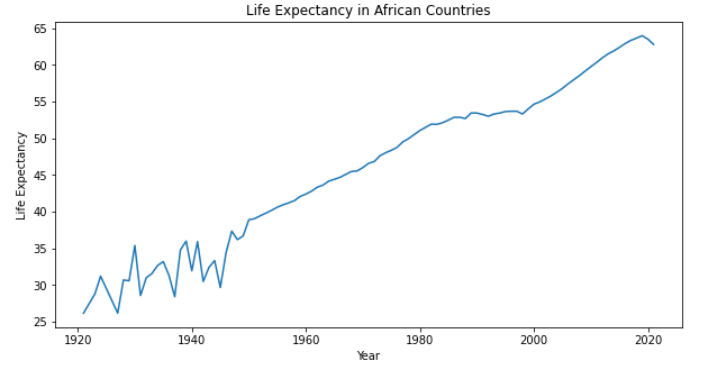
Question 4: What is the trend for life expectancy in African countries based on historical data?
Question 7: How does life expectancy affect GDP and Poverty and vise versa
Question 1: What is the distribution of poverty across African countries?
Insight
The dataset reveals that there is a wide range of poverty levels across African countries. Some countries, such as the Democratic Republic of Congo (COD), the Central African Republic (CAF), and Mozambique (MOZ) and a few others have almost 40-50% of their population earning a daily income of less than one dollar.
On the other hand, majority of countries in Africa have up to 50% of their total population earning between one dollar and two dollars and fifteen cents. These findings highlight the need for more targeted poverty reduction efforts and policies that focus on improving income levels in these countries.
Question 2: Which African countries have the highest and lowest GDP?
Insights
Based on the analysis of the GDP data for African countries in 2021, we can see that Nigeria (NGA) has the highest GDP followed by South Africa (ZAF) and Egypt (EGY). These countries are among the most populous on the continent and have some of the largest economies.
On the other hand, countries like Sao Tome and Principe (STP), Comoros (COM), and Seychelles (SYC) have the lowest GDPs among African countries in 2021.
Question 3: Which African countries have the highest and lowest life expectancy?
Insights
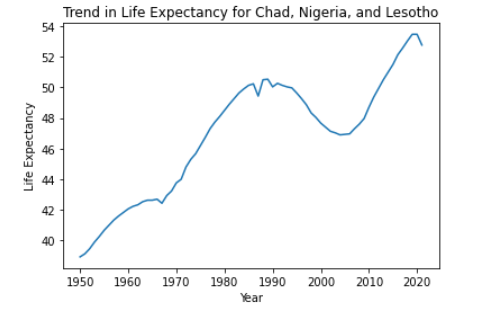
Based on the data, we can see that some African countries have a relatively high life expectancy at birth, such as Algeria DZA (76.4 years), Cape Verde CPV (74.1 years), and Morocco MAR (74.0 years). However, other countries, such as Chad TCD (52 years), Nigeria NGA (53 years), and Lesotho LSO (53 years), have much lower life expectancies.
The differences in life expectancy between these countries may be attributed to various factors, including healthcare access, disease prevalence, and lifestyle factors. Countries with higher life expectancies may have better access to healthcare and disease prevention measures, while countries with lower life expectancies may face challenges in providing adequate healthcare and managing infectious diseases.
To improve life expectancy in African countries with lower rates, efforts could be made to improve healthcare infrastructure and disease prevention measures. Additionally, education campaigns to promote healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise and healthy eating, could also help improve overall health outcomes.
Question 4: What is the trend for life expectancy in African countries based on the historical data?
Insights
Based on the available data from 1921 to 2021, we can see that there has been a general trend of increasing life expectancy in African countries over the years. In the 1920s, the average life expectancy was around 25-30 years, but this number has risen significantly to an average of 62 years in 2021. This increase can be attributed to various factors such as advancements in healthcare, better access to education and information, improved living conditions, and disease prevention efforts.
However, with continued efforts towards improving healthcare infrastructure and education, it is hoped that the trend of increasing life expectancy in African countries will continue in the coming years.
#
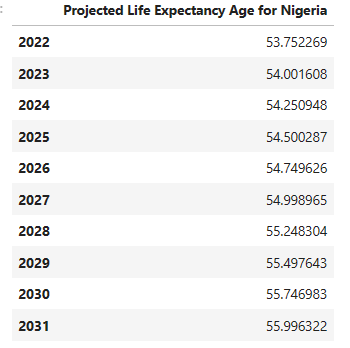
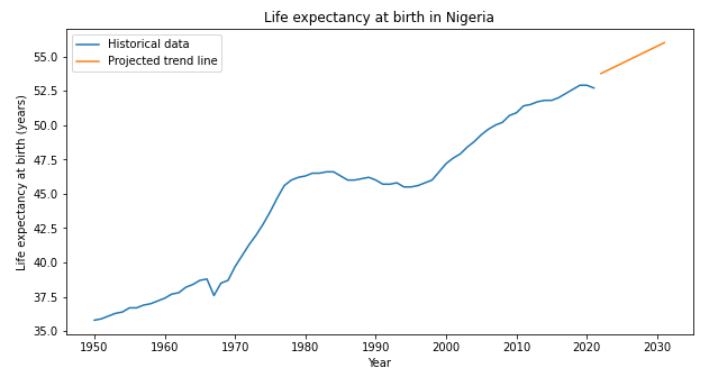
Question 5: What is the projected trend for life expectancy in African countries based on historical data?
We would put our emphasis on 3 countries with lowest life expectancy (Chad, Nigeria and Lesotho)
We then made projections for Nigeria
We predicted for next 10 years
Insights
Based on the analysis of historical data from 1950 to 2021 and the projections made for the next 10 years, it can be observed that there could be a gradual increase in life expectancy in Nigeria, which can be attributed to various factors such as improved healthcare facilities, increased access to education and information, better nutrition, and advancements in medical technologies.
However, there are still challenges to be addressed to improve the overall life expectancy rate in Nigeria, such as reducing infant mortality rates, improving access to clean water and sanitation, and increasing public awareness of health issues.
Therefore, it is important for the federal government (FGN) to continue investing in healthcare infrastructure and promoting health education and awareness to sustain the current trend and improve the overall health of the population.
#
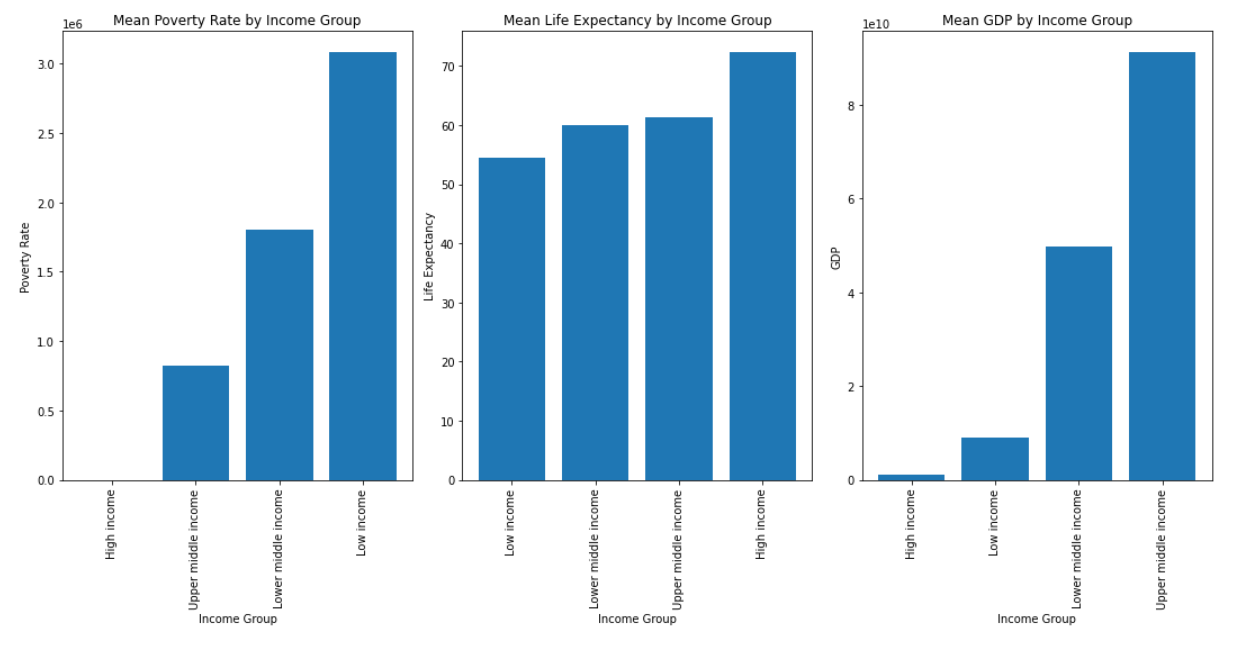
Question 6: How do poverty, life expectancy, and GDP vary across different income groups in all countries?
Insights
Poverty, life expectancy, and GDP vary across different income groups in all countries.
Wealthier countries tend to have lower poverty rates, higher life expectancies, and higher GDPs. The poorest countries have the highest poverty rates, lowest life expectancies, and lowest GDPs. There is a great deal of variation within each income group.
The relationship between poverty, life expectancy, and GDP is clear. Wealthier countries tend to have lower poverty rates, higher life expectancies, and higher GDPs. This is because wealth can be used to invest in things like healthcare, education, and infrastructure, all of which contribute to improved health and well-being.
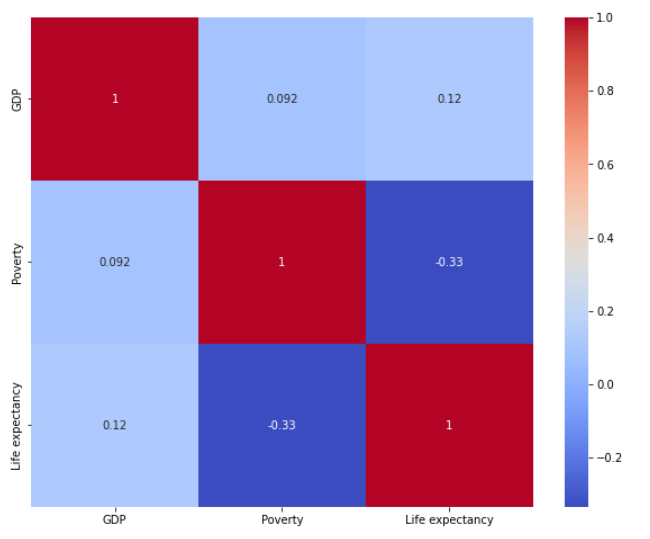
Question 7: How does life expectancy affect GDP and Poverty and vise versa?
Insights
GDP and life expectancy are positively correlated. This means that countries with higher GDPs tend to have higher life expectancies. This is likely due to a number of factors, such as better access to healthcare, education, and nutrition in wealthier countries.
GDP and poverty are weakly positively correlated. This means that countries with higher GDPs tend to have slightly lower levels of poverty. This is likely due to the fact that wealthier countries have more resources to invest in social programs and infrastructure, which can help to reduce poverty.
Poverty and life expectancy are negatively correlated. This means that countries with higher poverty rates tend to have lower life expectancies. This is likely due to the fact that people who are poor are more likely to live in unhealthy environments, have less access to healthcare, and have lower incomes, which can all contribute to shorter life expectancies.
Conclusions
Poverty
Poverty is a major problem in Africa, with over 40% of the population living on less than one dollar ninety cents a day.
The distribution of poverty is uneven, with some countries, such as the Democratic Republic of Congo and Mozambique, having much higher poverty rates than others.
There are a number of factors that contribute to poverty in Africa, including conflict, corruption, and climate change.
Life expectancy
Life expectancy in Africa has been increasing in recent years, but it is still lower than the global average.
The highest life expectancies are found in countries with the highest GDPs, such as Algeria and Morocco.
The lowest life expectancies are found in countries with the lowest GDPs, such as Chad and Lesotho.
GDP
GDP per capita in Africa has been increasing in recent years, but it is still lower than the global average.
The highest GDPs are found in countries with the largest populations, such as Nigeria and South Africa.
The lowest GDPs are found in countries with the smallest populations, such as Sao Tome and Principe and Seychelles.
In Conclusion, There is a clear relationship between poverty, life expectancy, and GDP in Africa.
- Countries with higher GDPs tend to have lower poverty rates, higher life expectancies, and better healthcare and education systems.
- Countries with lower GDPs tend to have higher poverty rates, lower life expectancies, and poorer healthcare and education systems.
There are a number of challenges that need to be addressed in order to reduce poverty, improve life expectancy, and improve GDP in Africa. These challenges include conflict, corruption, climate change, and lack of access to education and healthcare.
Despite the challenges, there is reason to be optimistic about the future of Africa. Africa has a young and growing population, and it is rich in natural resources. With the right policies and investments, Africa can continue to grow and develop, and it can improve the lives of its citizens.
Recommendations
Africa is a vast and diverse continent with a population of over 1.2 billion people. It is also a continent with a great deal of potential, with abundant natural resources and a young and growing population. However, Africa also faces a number of challenges, including poverty, hunger, disease, and conflict.
There are a number of things that can be done to improve economic and social conditions in Africa. These include:
Investing in education and healthcare: Education and healthcare are essential for economic growth and development. By investing in these sectors, African countries can improve the skills and productivity of their workforce and reduce the burden of disease.
Promoting good governance: Good governance is essential for attracting investment and creating a stable and predictable environment for businesses. African countries need to strengthen their institutions and fight corruption in order to promote good governance.
Encouraging trade and investment: Trade and investment are essential for economic growth. African countries need to open their markets to trade and investment and create an environment that is attractive to businesses.
Addressing climate change: Climate change is a major threat to Africa. By addressing climate change, African countries can protect their natural resources, reduce the risk of disaster, and improve the lives of their people.
Promoting peace and security: Peace and security are essential for economic growth and development. African countries need to resolve their conflicts and build strong institutions that can maintain peace and security.
These are just a few of the things that can be done to improve economic and social conditions in Africa. By taking these steps, African countries can create a better future for their people.